Detailed Explanation of Wire Bonding: A Comprehensive Guide to Electronic Interconnection Technology
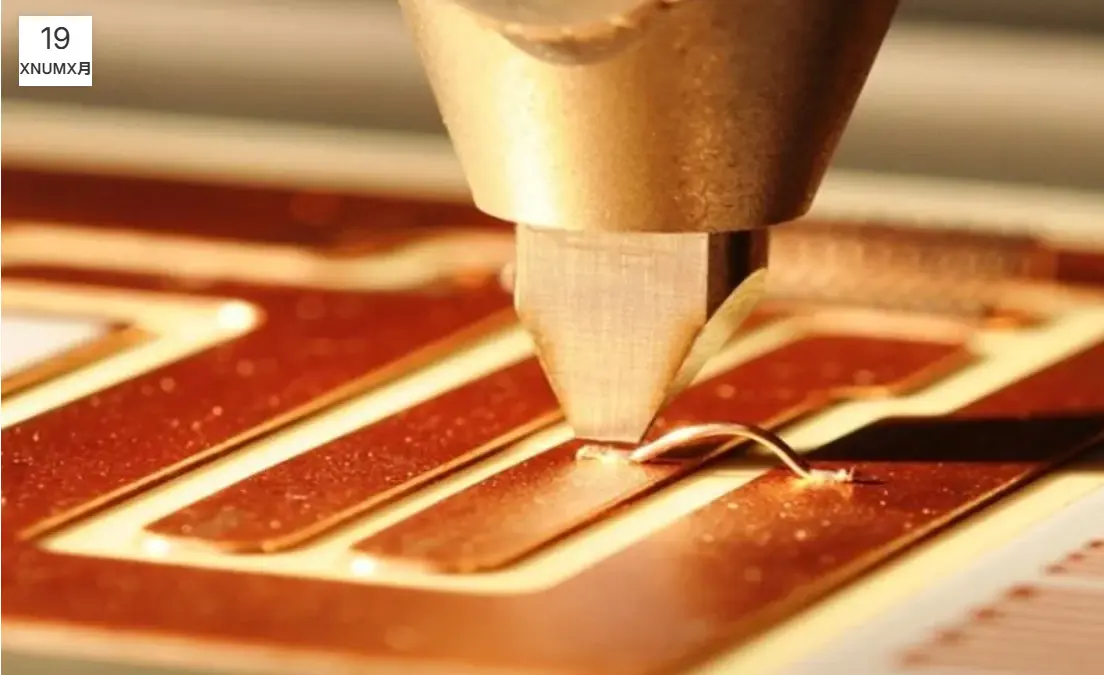

What is Wire Bonding?
Wire bonding is one of the microelectronic connection technologies used to connect or bond semiconductor devices to their packaging or substrates. This technology is one of the most important in the semiconductor industry, as it ensures that most chips can connect to external circuits in various electronic devices. With advancements in the electronics field, the practical application of new technologies such as flip-chip bonding is evident in today’s market.
Materials Used in Wire Bonding
The selection of wire materials is a key aspect of the wire bonding process, with each material having its unique advantages and disadvantages:
-
Gold (Au)
Gold wire is commonly used for wire bonding due to its excellent conductivity, high corrosion resistance, and ease of bonding. -
Aluminum (Al)
Aluminum wire is primarily used for wedge bonding because it offers better conductivity than gold and is relatively cost-effective. -
Copper (Cu)
Copper wire has higher electrical and thermal conductivity compared to aluminum and gold. -
Silver (Ag)
Silver wire is rarely used for wire bonding due to its high conductivity.
Types of Wire Bonding
Wire bonding can be divided into three main types, each with specific applications:
-
Thermosonic Ball Bonding
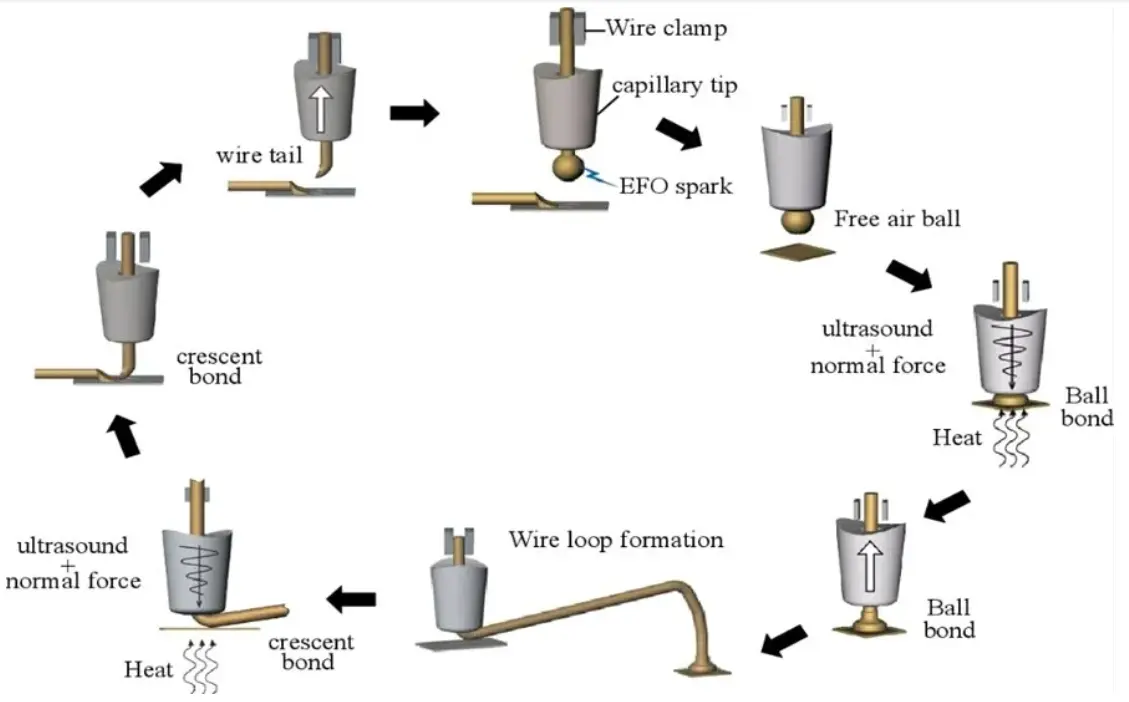
Thermosonic ball bonding is a widely used wire bonding method, especially for gold (Au) and copper (Cu) wires. In this method, ultrasonic energy, heat, and mechanical pressure are used to form a strong bond. The process begins by heating the end of the wire until it becomes spherical. Pressure is then applied to the bonding pad of the semiconductor device while ultrasonic vibrations and moderate heat are introduced. This combination creates a proper metallurgical bond that is very strong. -
Wedge Bonding
Wedge bonding commonly uses aluminum (Al) and gold wires. The ball bonding process starts with the formation of a ball, while the wedge bonding process begins with a flat bond. This technique involves ultrasonic energy and mechanical pressure but generates less heat. The traditional process for efficient wire bonding involves a wedge tool that presses the wire onto the bonding pad, with the remaining wire bonding achieved through ultrasonic vibrations. -
Thermocompression Bonding
Thermocompression bonding involves the use of heat and pressure without introducing ultrasonic energy. The wire and bonding pad are heated to high temperatures to facilitate diffusion bonding. This method is slower but allows for better temperature control.
Wire Bonding Process
The wire bonding process involves several key steps, each designed to ensure the establishment of reliable and effective electrical connections:
-
Chip Placement
The process begins with the correct positioning of the semiconductor chip onto the substrate of the package or lead frame. This step is crucial, as any discrepancies at this stage can affect the subsequent wire bonding steps. The chip is typically bonded using chip adhesive materials, which can be epoxy resin or solder, depending on the type and application of the package. -
Wire Material Selection
The choice of wire type and diameter is critical. This includes the wire’s electrical conductivity, thermal coefficient, and mechanical strength, all of which are essential for the wires used in manufacturing these devices. -
Tool Setup
The bonding tool, often referred to as a capillary for ball bonding techniques, plays an important role in the geometry, material, and wire material of the wire bonding tool. -
Bond Formation
The thermosonic ball bonding process begins by forming a free air ball (FAB) at the end of the wire through melting. Ultimately, the FAB is bonded to the chip pad with the help of ultrasonic energy, heat, and pressure. -
Loop Formation
The bonding tool moves to the location of the second bonding point, during which it moves in the form of a wire loop. The geometry and cross-sectional area of the wire loop are adjusted to ensure mechanical stability and the required electrical performance of the wire loop. -
Second Bond Formation
The second bond is formed at the location on the package substrate or lead frame where the chip is to be installed. In ball bonding, this means simply placing or contacting the wire to the bonding point with the bonding tool and then applying ultrasonic energy to form the stitch bond. -
Inspection and Testing
After completing the wire bonding process, some form of testing is conducted to check the quality or reliability of the bond. Common inspections include visual checks, tensile tests to display adhesive pull strength, and adhesive shear strength tests.
Applications of Wire Bonding
Wire bonding is widely used across various industries, demonstrating its versatility and reliability:
-
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, wire bonding connects semiconductor chips to packages in gadgets such as smartphones, portable tablets, laptops, and other portable devices. Therefore, due to its cost-effectiveness and efficiency, this technology is suitable for mass production in the consumer electronics sub-industry. -
Automotive Electronics
In automobiles, wire bonding is used for MCUs, sensors, power modules, and many critical components. The application of wire bonding in automotive electronics is vital due to its complementary characteristics, such as high tolerance to environmental conditions like temperature and humidity. -
Aerospace and Defense
Military and aerospace-related products require highly reliable electronic components that can survive even in the harshest conditions. Wire bonding is widely used in radar equipment, communication devices, and missile control systems. -
Medical Devices
Medical applications include pacemakers, hearing aids, electronic-controlled implants, and diagnostic equipment, where wire bonding is crucial for establishing good electrical connections. Due to the reliability and accuracy of wire bonding, it is highly suitable for life-sensitive circuits with virtually no failure rates.
Future Trends in Wire Bonding
As the electronics industry continues to evolve, several trends are shaping the future of wire bonding:
-
Miniaturization
With the trend toward miniaturization in the market, there is a need for micro and efficient wire bonding in global electronic devices. Recently, improvements in the types of bonds, bonding methods, and materials used have made it possible to produce fine-pitch wire bonds. -
Use of Copper Wire
The use of copper wire has been increasing over the years, marking a crossover point between the two wire choices. Copper wire is gradually replacing aluminum wire in wire bonding due to its superior electrical and thermal conductivity. -
3D Packaging
With the emergence of 3D packaging technologies such as System-in-Package (SiP) and Multi-Chip Modules (MCM), wire bonding technology has become the preferred solution for cost-effective and stringent requirements. -
Automation and AI Integration
Automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are widely applied in today’s wire bonding applications. AI implemented in wire bonding machines can automatically adjust bonding parameters, improve yield rates, and enhance bonding quality.
Conclusion
Wire bonding is one of the key operations in semiconductor packaging, referring to the formation of connections between the external leads of a chip and external circuits. This technology is fundamental and widely used in microelectronic products to ensure their efficiency and stability. The main advantages of wire bonding include low cost, versatility, and the ability to make small connections. The methods may include ball bonding, wedge bonding, and ribbon bonding, depending on the type and performance level of the materials used.
Thus, wire bonding remains an indispensable fundamental technology in semiconductor processing, continuously improving to meet the new demands of miniaturization and high-speed devices. Ongoing technological advancements are crucial for the development of microelectronics, which are thriving across various fields, from communication devices to aerospace.
Contact Us
For any questions regarding our products or solutions, kindly entrust them to us and we will respond within 24 hours.
KeyWords
Wedge Bonding ToolWedge Tool
Bonding Wedge
Au Wire Bonding
Concave wedge Tool
Wedge Bonding Machines
Wire Bonding ToolsBonding Equipment SuppliersFine Pitch Bonding ToolsWedge BonderWire bonding equipmentSemiconductor bonding toolsPrecision bonding toolsHigh-performance wire bonding toolsSemiconductor industry toolsBonding tool manufacturerCustomizable wire bonding solutionsQuality wedge bonding equipment





