In the rapidly evolving semiconductor industry, the Wire Bond Machine plays a vital role in ensuring efficient production. Dr. Alice Wong, a leading expert in semiconductor manufacturing, once stated, "Quality wire bonding is the backbone of reliable electronic devices." This highlights the importance of selecting the right wire bonding equipment.
Choosing a Wire Bond Machine can be challenging. With numerous options available, each machine offers varied capabilities and features. The intricacies of wire bonding can affect the overall performance of semiconductors. For instance, issues like bond strength and reliability can stem from using subpar machines. Every detail matters in this delicate process.
As we explore the top ten wire bond machines, it is essential to consider both advanced features and potential shortcomings. Each machine brings unique advantages, yet certain models may not fully meet the demands of high-volume production. Reflecting on these aspects can guide manufacturers in making informed choices that cater to their specific needs and enhance their operational efficiency.

Wire bond machines play a crucial role in semiconductor manufacturing. They connect semiconductor chips to external circuitry using fine wires. In this industry, efficiency is key. A recent report found that the global wire bonding equipment market is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing demand for electronic devices. This growth puts pressure on manufacturers to optimize their processes.
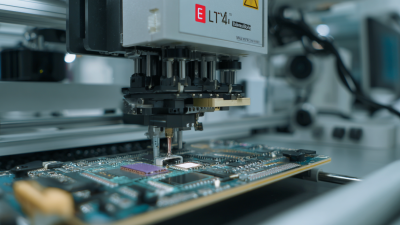
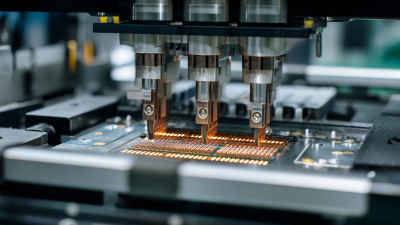
Wire bond technology continues to evolve. The latest machines offer advanced features, such as automatic wire feed and real-time monitoring. These advancements improve yield rates and reduce defects. However, the complexity of these machines poses challenges. Operators need to be well-trained to manage them effectively. With a high level of precision required, even minor errors can lead to costly failures.
Moreover, the industry faces challenges in supply chain management. Components for these machines can be difficult to source, impacting production timelines. Manufacturers must strike a balance between investing in new technology and maintaining operational efficiency. As the demand for semiconductor products rises, the pressure to improve wire bonding processes will only increase. Adapting to these changes is essential for success in this competitive landscape.
When selecting the right wire bond machine, it's crucial to consider key features that optimize semiconductor production. Modern machines should offer precision bonding capabilities. The capability to handle ultra-fine wires ensures improved connections with smaller components. Industry reports indicate that a growing demand for miniature electronics is pushing manufacturers to seek machines capable of high accuracy. More efficient bond patterns can enhance overall yield rates.
Additional features to watch for involve automation and flexibility. Machines that allow quick changeovers can significantly reduce downtime. Data suggests that companies utilizing flexible systems increase productivity by up to 30%. Look for features like adjustable bonding temperatures and speeds, accommodating different materials frequently used in the industry.
Tip: Regular maintenance is often overlooked but critical for performance. Keeping the machine calibrated can prevent errors and enhance longevity.
Another consideration is the power consumption of these machines. Energy-efficient models not only reduce costs but also support sustainability initiatives. Reports show that the semiconductor sector is gradually moving towards greener technology. Investing in energy-efficient equipment might also lead to higher operational ratings.
Tip: Always evaluate your production needs before making a purchase. Not all machines will meet specific operational requirements effectively.
Selecting a wire bond machine is critical for semiconductor production. Performance varies widely among models. Each machine features different specifications that can impact efficiency. Consider the bonding speed and accuracy ratings. These factors determine how well the machine will perform in a production environment.
Workflow integration is vital when choosing a machine. The ease of setup and operation can aid in reducing downtime. Complex interfaces may lead to operational mistakes. If operators struggle, the production line slows down. It’s not just about speed; reliability matters. A machine that misfires creates waste and increases costs.
Additionally, maintenance requirements should be weighed. Some machines demand frequent servicing, while others operate smoothly for extended periods. Reflect on the potential trade-offs. An advanced machine might offer high speed but at the cost of upkeep. Balancing performance and maintenance is essential for successful manufacturing.
When examining the cost and efficiency of leading wire bond machines, various factors come into play. Recent industry reports highlight that the average cost of a wire bond machine ranges from $50,000 to $250,000. However, the return on investment (ROI) often depends on the machine's performance. Machines with higher throughput can bond over 10,000 connections per hour, significantly increasing production rates.
Efficiency also varies based on technology. For example, automated systems tend to reduce labor costs by up to 30%. Yet, initial setup and calibration can sometimes lead to inefficiencies, requiring tools and adjustments that are time-consuming. Additionally, manufacturers face challenges like machine downtime due to maintenance. Reports indicate that unplanned maintenance can cause production losses of up to 20%, which is a critical consideration for decision-makers.
Moreover, the advent of advanced materials affects efficiency. Some newer machines can handle materials that traditional ones cannot. This can lead to an increase in costs but also offers a chance for a competitive edge. Balancing cost and efficiency remains a complex task for semiconductor producers, and the pursuit of the optimal wire bond machine continues to evolve.
| Machine Type | Cost ($) | Efficiency (Wires/min) | Bonding Technology | Footprint (sq. ft.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | $100,000 | 300 | Thermal | 10 |
| Model B | $120,000 | 350 | Ultrasonic | 12 |
| Model C | 150,000 | 400 | Thermal | 8 |
| Model D | 80,000 | 280 | Ultrasonic | 11 |
| Model E | 110,000 | 360 | Thermal | 9 |
| Model F | 130,000 | 370 | Ultrasonic | 10 |
| Model G | 95,000 | 320 | Thermal | 12 |
| Model H | 115,000 | 340 | Ultrasonic | 9 |
| Model I | 105,000 | 330 | Thermal | 10 |
| Model J | 125,000 | 390 | Ultrasonic | 11 |
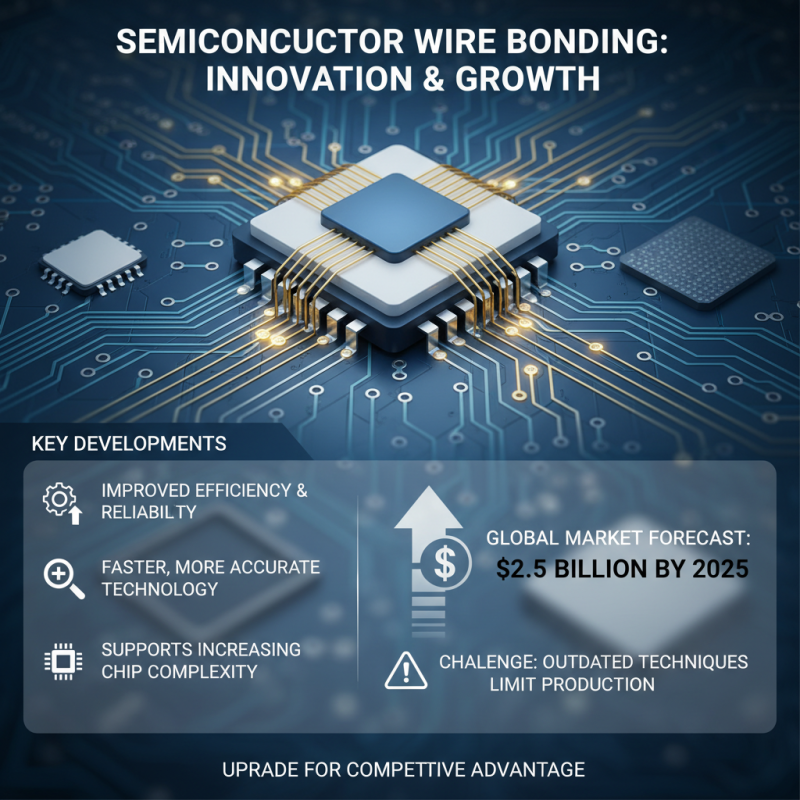
The wire bonding process plays a crucial role in semiconductor production. Recent advancements focus on improving efficiency and reliability. As chip complexity increases, the demand for faster and more accurate wire bonding technology is skyrocketing. Industry reports reveal that the global wire bonding market is expected to reach $2.5 billion by 2025. However, many manufacturers still rely on outdated techniques that limit production capabilities.
Automation is becoming a significant trend in wire bonding technology. Automated systems can enhance precision and reduce human error. A report from a well-known semiconductor research firm indicates that automated wire bonding can improve throughput by up to 30%. Despite these improvements, the implementation costs and the need for skilled workers pose challenges that must be addressed.
Another trend is the adoption of new materials and processes. For instance, ultrasonic and thermosonic bonding methods are gaining traction. These methods allow for better connections with thinner wires. Yet, there are concerns about compatibility with existing production lines. Many factories are hesitant to shift due to potential operational disruptions. The evolution of wire bonding technology is promising, but it requires careful consideration of current capabilities and future needs.