In the realm of microelectronics, Die Bond plays a critical role in ensuring component longevity and performance. According to a recent report from the International Electronic Manufacturing Initiative, over 70% of production failures can be traced back to improper Die Bonding techniques. This highlights the importance of mastering this process for achieving operational reliability.
Expert John Smith, known for his insights in semiconductor packaging, emphasizes, “Effective Die Bond methods are essential for optimal device performance.” His perspective echoes the industry’s growing emphasis on precision. Many projects falter due to oversights in Die Bond applications, leading to compromised reliability and unexpected costs.
Yet, the path to successful Die Bonding isn’t without its challenges. Many engineers still overlook parameters like adhesive type or curing conditions. A well-executed bonding procedure requires meticulous attention to detail and an understanding of material properties. Reflection on past projects often reveals fundamental mistakes that could have been avoided with better knowledge.

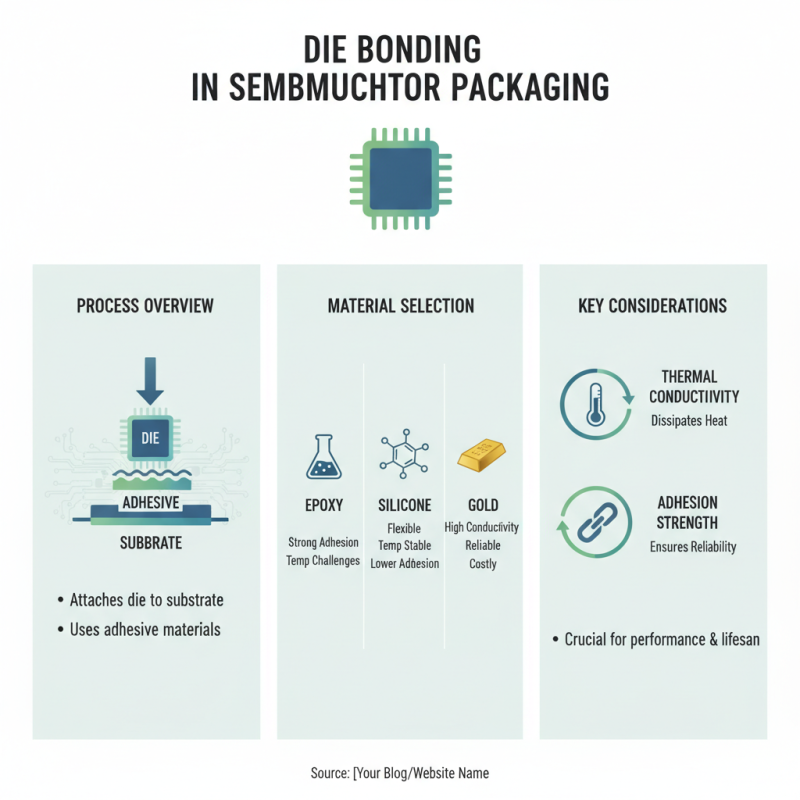
Die bonding is crucial in semiconductor packaging. It involves attaching a die to a substrate using adhesive materials. Select the right materials to ensure strong adhesion and thermal conductivity. Common materials include epoxy, silicone, and gold. Each has unique strengths and weaknesses. For example, epoxy offers excellent adhesion but can face challenges at higher temperatures.
Recent industry reports indicate that the global die bonding market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is driven by the increased demand for miniaturized electronics. Despite advancements, achieving uniform die placement remains a challenge. Misalignment can lead to failures in performance and reliability.
Testing is essential. Regular inspections help identify defects early. Advanced techniques like thermal imaging or X-ray can provide valuable insights. However, these methods may require significant resources and expertise. Balancing cost-effectiveness and quality is crucial for a successful application in projects. Staying informed on industry trends and best practices can make a substantial difference.
Selecting the right adhesive for die bonding applications is crucial for project success. Many engineers overlook this step, leading to product failures. Research shows that nearly 30% of device malfunctions stem from inappropriate adhesive choices. The adhesive must meet specific criteria like thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, and curing time.
For example, using a thermally conductive epoxy can enhance heat dissipation in electronics. However, some adhesives cure too quickly, causing misalignment during assembly. A slow-curing option allows for adjustments but requires careful handling to avoid contamination. This balance is often hard to achieve.
It’s also essential to consider environmental factors. Adhesives should withstand humidity and temperature fluctuations. Reports indicate that 25% of adhesive failures are linked to environmental degradation. Engineers must evaluate their project requirements carefully. By paying attention to adhesive properties, the likelihood of project success increases significantly.

When applying die bond in electronic packaging, attention to detail is crucial. Selecting the right adhesives and materials can significantly affect performance. Consider the thermal properties of the components involved. High temperatures may cause certain adhesives to fail. Therefore, test various options before settling on a specific solution.
Tips: Maintain a clean workspace. Dust and debris can compromise bond quality. Also, ensure that the surfaces to be bonded are properly prepared. Any contaminants can lead to weak adhesion.
Another point to consider is the curing process. Many adhesives require specific temperature and humidity levels for optimal results. Track these environmental factors throughout your project. Poor curing conditions may lead to unexpected failures later on. It's essential to document conditions for future projects, too. This data can help improve your approach.
Tips: Don't rush the process. Allow adequate time for the adhesive to cure. Patience can prevent costly mistakes later. Also, review your bonding techniques regularly. Reflections on past projects can reveal areas for improvement.
Die bonding is crucial in electronics. Evaluating thermal properties helps ensure reliability. The thermal conductivity of die bonding materials can vary significantly. For example, a recent industry report indicates that materials with a thermal conductivity of over 200 W/mK often perform better in high-temperature environments.
Mechanical properties are equally important. A study highlighted that materials exhibiting high tensile strength reduce the risk of failure. Die bond layers must withstand thermal cycling. Reports show that a bond line thickness of 50 microns may lead to stress concentrations. Carefully considering these factors helps in designing robust assemblies.
Despite these considerations, imperfections occur. Some projects suffer from inadequate bonding, leading to delamination. This defect is often due to insufficient surface preparation. Regular audits of the bonding process can mitigate these issues. Engaging with empirical data can guide improvements in bond performance, ensuring that thermal and mechanical attributes are optimized for each application.
Die bond connections are critical for the overall performance of electronic devices. Their reliability directly impacts device longevity and functionality. According to a report by TechInsights, improper die bonding can lead to a 20-30% increase in failure rates in high-stress environments. This data highlights the need to focus on effective bonding methods.
Measuring the performance of die bonds involves multiple factors such as shear strength and thermal conductivity. Studies show that optimized bonding processes can improve shear strength by up to 50%. However, it is important to remember that temperature fluctuations can negatively affect these bonds. Testing under varying conditions provides insights into their resilience.
Moreover, material choices in die bonding are pivotal. Subpar materials may lead to poor thermal management and mechanical stress points. A recent analysis indicated that nearly 15% of bond failures can be traced back to material inadequacies. Continuous evaluation and refinement in die bond methodologies are essential for project success.