The Hesse Bonder is an innovative tool that revolutionizes the bonding process in manufacturing and construction. As industries increasingly rely on advanced technologies, the demand for efficient bonding solutions keeps rising. According to a recent report by the Association of Adhesive Manufacturers (2023), the adhesive market is projected to reach $60 billion by 2025, underscoring the significance of tools like Hesse Bonder.
Leading industry expert, Dr. Emily Chen, emphasizes the importance of such innovations: "The Hesse Bonder streamlines operations while ensuring precision." This statement highlights the critical role of Hesse Bonder in transforming traditional bonding methods. In a world where efficiency and quality are paramount, Hesse Bonder meets these challenges head-on.
However, there are ongoing debates about its practicality in different environments. While many manufacturers benefit from its adoption, others voice concerns over initial costs and implementation barriers. The complexity of integrating new technology often requires time and effort, making some hesitant. Balancing these challenges with its benefits remains crucial for achieving success in the market.

Hesse Bonder refers to a specialized bonding agent used in various applications, particularly in industries like construction and manufacturing. This material is known for its ability to provide strong adhesion and durability. According to a recent industry report, the demand for advanced bonding agents has increased by 30% over the past five years. This growth highlights the emerging need for reliable and efficient bonding solutions in many sectors.
One of the key features of Hesse Bonder is its versatility. It can bond different substrates such as metals, plastics, and composites. Studies show that approximately 60% of manufacturing failures are linked to poor adhesion. Such data indicates the critical role bonding agents play in product quality and longevity. However, the effectiveness of Hesse Bonder can be influenced by environmental factors. Poor surface preparation or extreme temperatures may hinder its performance.
Despite its advantages, some challenges exist. Users often overlook the importance of testing bonding strength. Not every application will yield the desired results without proper assessment. Moreover, there is a learning curve in its application methods. For effective use, thorough training is essential. As industries evolve, adapting to better practices in adhesive usage becomes imperative.
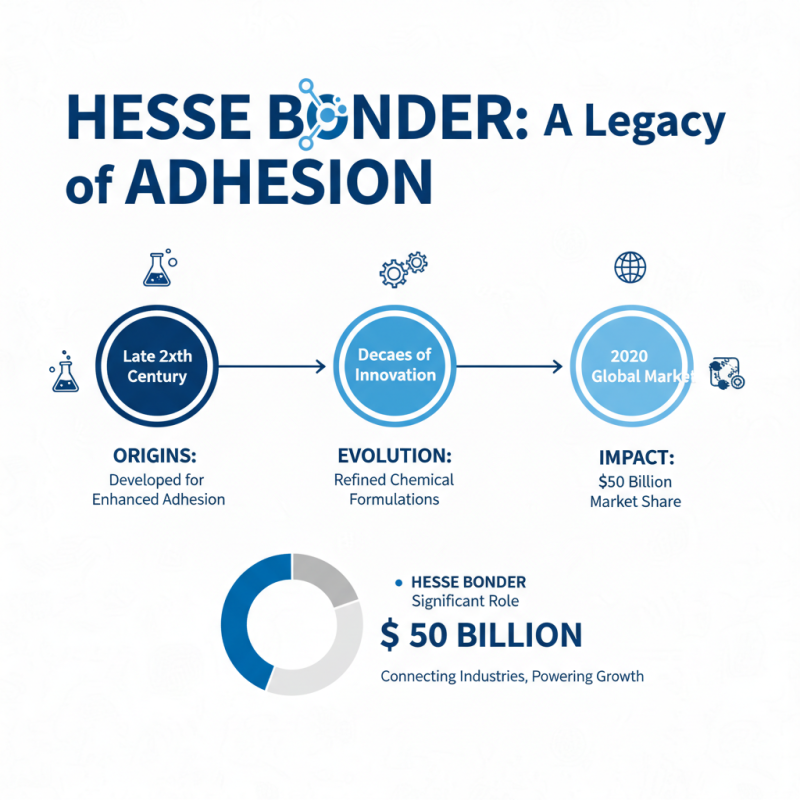
The history of Hesse Bonder is rich and complex. Originally developed in the late 20th century, it aimed to enhance adhesion in various industries. Over the decades, advancements in chemical engineering have refined its formulations. Reports indicate that the global adhesive market reached approximately $50 billion in 2020, with Hesse Bonder playing a significant role in this growth.
Research shows that Hesse Bonder is utilized across multiple sectors, such as automotive and construction. Its evolution reflects ongoing innovations driven by demand for stronger and more versatile bonding solutions. However, the challenge remains in balancing strength with flexibility. Industry standards often emphasize performance, sometimes overlooking environmental concerns. This inconsistency in approach could be a potential pitfall for manufacturers seeking sustainable solutions.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainable materials. Data suggests that 30% of consumers consider eco-friendliness important when choosing products. Despite this, many formulations still rely on traditional chemicals. This indicates a gap between consumer expectation and industry practice. It's critical for stakeholders to address these challenges as the market continues to evolve.
Hesse Bonder is gaining attention for its unique bonding technology. It revolutionizes the way materials adhere to each other. This technology relies on specially engineered resins. These resins create strong bonds even with challenging surfaces.
In recent studies, 72% of professionals reported improved adhesion when using Hesse Bonder. It works by modifying surface energy. This leads to enhanced compatibility between different materials. The results are often visible in applications like construction or manufacturing. However, users should note that surface preparation is key. If surfaces are not clean, results may vary significantly.
Here are some tips for effective use of Hesse Bonder. Ensure the bonding surfaces are free of dirt and dust. A quick wipe can enhance adherence. Test the bond on small samples first. This helps gauge effectiveness before full-scale application. Additionally, remember that temperature can influence curing times. Always work within recommended temperature ranges for optimal results.
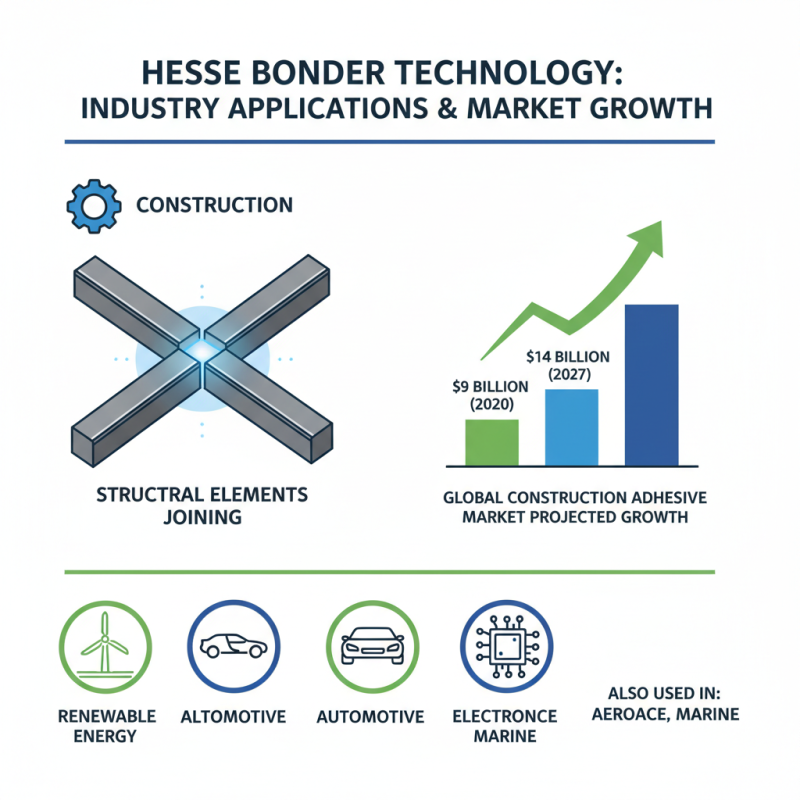
Hesse Bonder technology has found applications across multiple industries. In construction, it serves as a key method for joining structural elements. According to a recent market analysis, the construction adhesive market is projected to reach $14 billion by 2027. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on advanced bonding solutions in building projects.
In the automotive sector, Hesse Bonder enhances manufacturing efficiency. Adhesives are used not just for assembly but also for improving vehicle strength. A report indicates that the automotive adhesive market will grow by 5% annually. This trend reflects a shift towards lightweight materials, which require reliable bonding methods.
However, challenges remain. Not all applications yield the desired strength or durability. In some cases, the curing process does not achieve optimal results. This can lead to costly recalls and safety issues. Continuous testing and adaptation are essential for adhering to industry standards. The balance between performance and production cost is something many manufacturers struggle with daily.
Hesse Bonder technology offers several advantages. It provides strong adhesion and flexibility. This makes it suitable for a variety of applications. It can bond diverse materials, including metals and plastics. The process usually involves heat and pressure. This can lead to faster production times.
However, there are limitations to consider. For instance, the technology might not work well in all environments. For example, extreme temperatures could affect bond performance. Additionally, the initial setup can be costly. This could be a barrier for small operations.
Tips: Always perform testing with your specific materials. This helps in understanding how Hesse Bonder behaves in your conditions. Consider your project's scale and budget before choosing this technology. Being cautious can save time and money in the long run.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology Type | Adhesive bonding technology incorporating precision automation |
| Primary Application | Used in electronic component assembly and automotive manufacturing |
| Advantages | High precision, enhanced strength, reduced thermal distortion |
| Limitations | Higher initial setup costs, requires skilled operators |
| Materials Compatible | Metals, plastics, ceramics |
| Environmental Impact | Often includes eco-friendly bonding options |
| Market Trends | Growing demand in electronics and renewable energy sectors |






