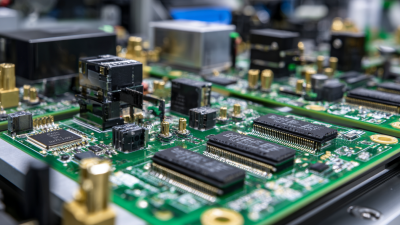
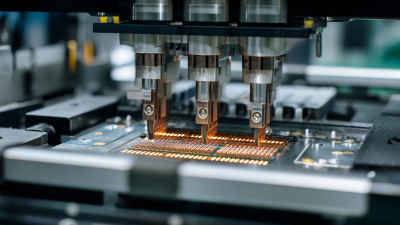
In the technological landscape of 2025, the importance of Gold Wire Bonding techniques has become increasingly pronounced, acting as a cornerstone in the semiconductor and electronics industries. According to Dr. Emily Roth, a leading expert in microelectronics, "Gold Wire Bonding is not just a manufacturing process; it's an art form that ensures the reliability and performance of electronic devices." This statement encapsulates the essence of Gold Wire Bonding, highlighting its critical role in connecting semiconductor chips to their packages with unparalleled efficiency and reliability.
As we delve deeper into the methodologies of Gold Wire Bonding, it becomes evident that advancements in this field have led to enhanced thermal and electrical conductivity, which are essential for the performance of modern electronic devices. The process of bonding gold wires is not merely a technical procedure; it requires a deep understanding of materials science and engineering principles. With the ever-increasing miniaturization of electronic components, mastering Gold Wire Bonding techniques is vital for manufacturers aiming to meet the growing demands for compact and efficient device designs. In this analysis, we will explore the intricate methodologies, emerging trends, and the future implications of Gold Wire Bonding technology in the next few years.
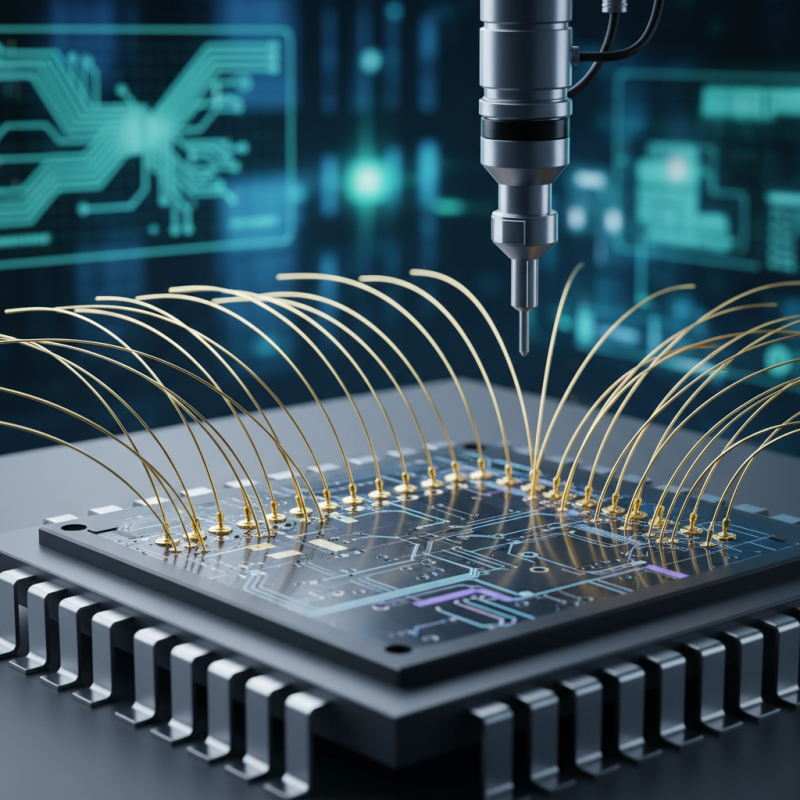
Gold wire bonding techniques play a crucial role in the semiconductor industry, particularly as we advance into 2025. These methods involve connecting wire bonds from semiconductor chips to their packages, ensuring reliability and performance in electronic devices. As technology progresses, the focus on enhancing efficiency, minimizing defects, and optimizing cost-effectiveness becomes paramount. In 2025, advancements in automation and precision techniques will further streamline the bonding process, leading to increased production rates and improved yield.
When working with gold wire bonding, it is essential to consider several factors that can impact the quality of the bond. One key tip is to ensure that the surface of the bonding pads is clean and free from contaminants to promote effective adhesion. Additionally, selecting the appropriate wire diameter plays a vital role in achieving optimal performance; thinner wires can be beneficial for tight spaces, while thicker wires may offer enhanced strength.
Another crucial aspect is the bonding parameters such as temperature, pressure, and time. Fine-tuning these settings can lead to significant improvements in bond strength and reliability. Always conduct tests to determine the ideal conditions for different applications, as this can help mitigate potential issues in high-stress environments. Keeping abreast of the latest techniques and innovations in the field will also empower manufacturers to maintain competitive advantages in an increasingly demanding market.

Gold wire bonding remains a crucial interconnection method in modern electronics, offering significant advantages that enhance the performance and reliability of electronic devices. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global wire bonding market is projected to reach $3 billion by 2025, with gold wire bonding accounting for a substantial share due to its superior properties. One of the primary benefits of gold wire bonding is its excellent conductivity, which ensures minimal signal loss and efficient power delivery. This is essential in high-frequency applications, where signal integrity is paramount.
Additionally, gold wire bonding boasts remarkable corrosion resistance, making it ideal for use in harsh environments. A study by IC Insights highlights that over 30% of electronic failures in automotive and industrial applications stem from poor interconnection materials. By utilizing gold, manufacturers can significantly mitigate these risks, enhancing product longevity and reducing maintenance costs. Furthermore, gold's malleability and ductility facilitate precise bonding in compact spaces, accommodating the ongoing trend of miniaturization in electronics. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of gold wire bonding in ensuring the reliability and performance of advanced electronic components is set to become even more critical.
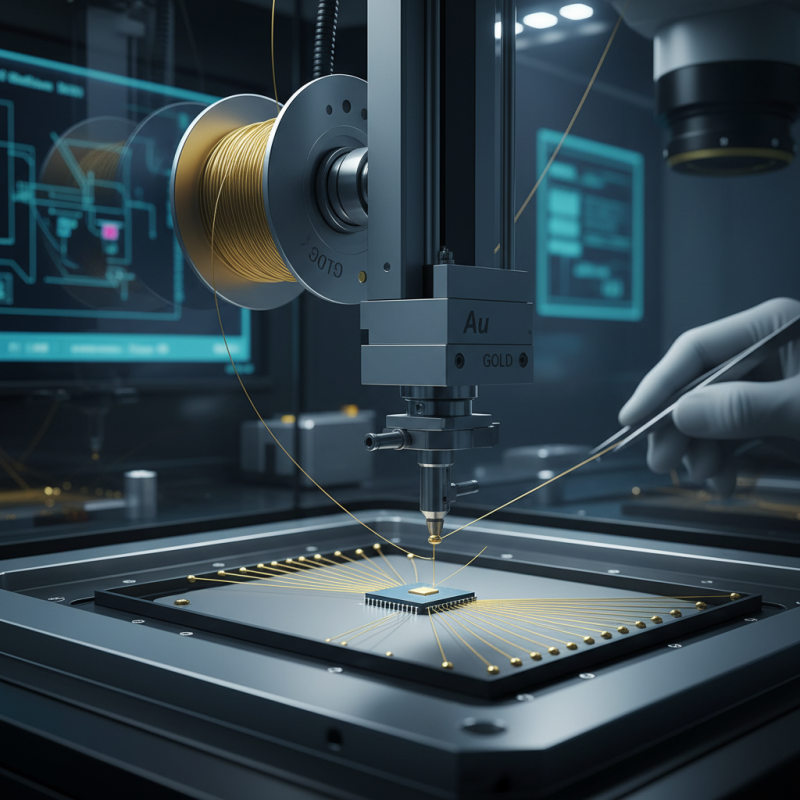
The gold wire bonding technique remains a critical method in semiconductor packaging, yet it faces significant challenges that could impact its efficacy and adoption in the future. One primary concern is the increasing cost of gold, which has seen fluctuations that mirror the global economic environment. According to a report by the International Monetary Fund, the price of gold is projected to rise by approximately 15% in the next few years, driven by demand in various sectors. This rise may compel manufacturers to explore alternative materials, potentially compromising the reliability that gold offers in wire bonding applications.
Additionally, advances in alternative bonding technologies, such as copper wire bonding and hybrid bonding methods, present competition that challenges the traditional dominance of gold. A study by Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International (SEMI) indicated that the adoption rate of alternatives like copper bonding methods has increased by over 25% in key sectors, including mobile devices and automotive electronics. These alternatives not only promise cost savings but also enhanced performance in certain scenarios, which may further dilute the market share of gold wire bonding.
Moreover, the miniaturization of electronic components necessitates more precise bonding techniques that can handle smaller geometries without sacrificing strength or reliability. As reported by the International Journal of Electronics Packaging, achieving consistent quality in bonding at reduced sizes has become a pressing engineering challenge. This, coupled with the need for sustainable practices as the industry moves towards more environmentally friendly processes, highlights that while gold wire bonding techniques remain essential, they must evolve to meet new economic and technical demands by 2025.
As we look ahead to 2025, the field of gold wire bonding is set to undergo significant transformations driven by advancements in technology and materials science. The post-pandemic landscape has catalyzed a demand for more reliable and efficient bonding methods, particularly as electronic devices become smaller and more complex. Innovations such as ultrasonic and thermosonic bonding are emerging, enhancing the ability to create stronger, more dependable connections while minimizing potential damage to delicate components. This evolution not only boosts the performance of electronic devices but also addresses environmental concerns by reducing the amount of gold used in production.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into the gold wire bonding process is gaining traction. These technologies enable more precise control over bonding parameters, resulting in improved yield rates and decreased production costs. Predictive analytics can help identify potential failures in the bonding process before they occur, thus increasing efficiency. As the industry moves toward increased automation and smart manufacturing, gold wire bonding is poised to become even more critical in the production of high-performance electronics, ensuring that communication and connectivity technologies meet the demands of future generations.
| Technique | Key Advantages | Potential Innovations | Industry Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic Bonding | High reliability and strong interconnections | Advanced ultrasonic transducer designs | Consumer electronics, automotive sensors |
| Thermosonic Bonding | Effective for heat-sensitive materials | Innovative materials for lower heat impact | Medical devices, aerospace components |
| Gold-Silver Bonding | Cost-effective with good electrical conductivity | New alloy compositions for improved performance | Telecommunication devices, smartphones |
| Plated Wire Bonding | Enhanced environmental resistance | Plating technology advancements | High-reliability markets, industrial applications |
| Mass Reflow Bonding | Higher throughput in production | Integration with automation technologies | Semiconductors, microelectronics |
Gold wire bonding is a critical technique in the manufacturing and assembly of electronic components, serving diverse industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, and telecommunications. In the automotive sector, for instance, robust and reliable connections are vital for ensuring the performance and safety of electronic control units. Gold wire bonding offers superior conductivity and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for high-temperature and harsh environment applications. This reliability is essential not only for traditional vehicles but also for electric and hybrid models that increasingly depend on sophisticated electronic systems.
In consumer electronics, gold wire bonding is paramount for enabling compact designs and enhanced performance. Devices like smartphones, tablets, and wearables require high-density interconnections, and gold wire bonding facilitates the miniaturization of components without compromising quality. Moreover, in the telecommunications industry, the rapid advancement of 5G technology demands high-performance components. Gold wire bonding techniques contribute to improved signal integrity and faster data transmission rates, critical for meeting the demands of next-generation communication systems. These applications underline the evolving significance of gold wire bonding across various industries in 2025 and beyond.