In the world of electronics, understanding the difference between bonding wire and ribbon is crucial. Dr. Emily Chen, an expert in semiconductor materials, once stated, "The choice of bonding method can significantly impact performance." Bonding Wire and Ribbon play vital roles in making connections within devices.
Bonding wire is thin and flexible, often made of gold or aluminum. It’s suitable for small, precise applications. Ribbon, on the other hand, is flat and broader, ideal for larger connections. The choice can influence not just performance, but also the reliability of electronic devices. Each has specific strengths and weaknesses.
Finding the right option requires careful consideration. As the industry evolves, so does the technology behind these materials. Yet, the proper application remains a challenge for many. Reflecting on the ongoing innovations in Bonding Wire and Ribbon can lead to better designs. The insights of experts like Dr. Chen guide these discussions.
Bonding wires and ribbons are essential components in electronic packaging. While both serve the purpose of making connections, they differ in form and function. Bonding wires are typically thin, round wires made of gold, aluminum, or copper. They are commonly used to connect semiconductor devices to their packages or substrates. Their smaller diameter allows for precise connections, making them suitable for densely packed circuits.
In contrast, bonding ribbons are flat, rectangular strips. They offer a larger surface area compared to wires, which can enhance bond strength. This can be particularly advantageous in applications where thermal performance is crucial. Ribbons are often used for larger chips or in larger assembly processes. Their shape allows for easier handling, but less precision compared to wires.
Choosing between bonding wire and ribbon often depends on specific application requirements. Each option has its pros and cons. Some engineers may find they struggle with bond reliability when using wires in certain conditions. On the other hand, ribbons might not fit into all designs. It’s important to consider these factors carefully.
This chart compares the electrical conductivity of bonding wires and ribbons made from copper and aluminum. Bonding materials vary in conductivity, impacting their effectiveness in electronic applications.
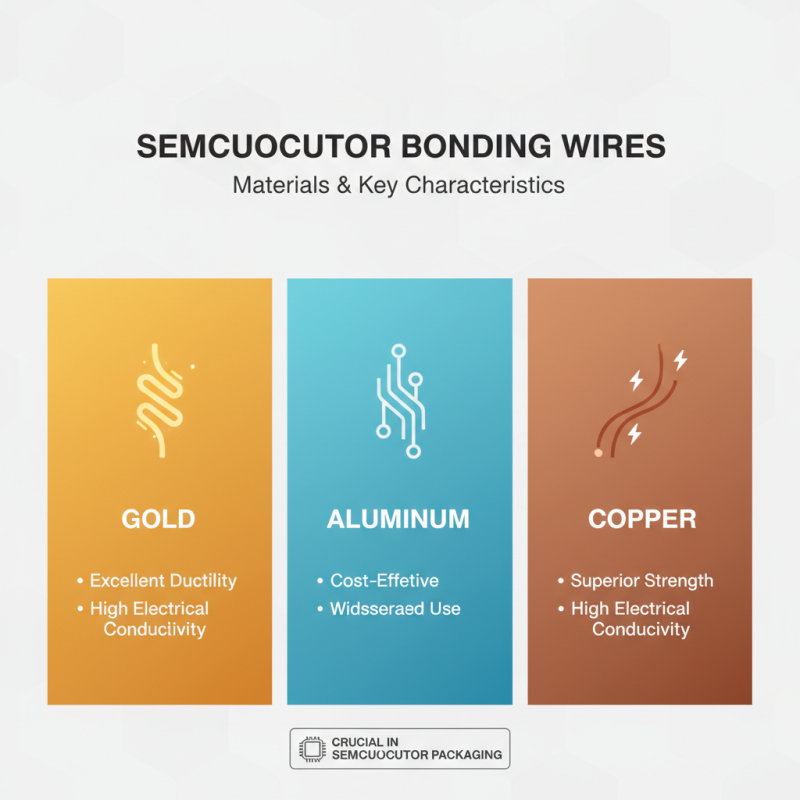
Bonding wires and ribbons play crucial roles in semiconductor packaging. The key characteristics of bonding wire include material composition and properties. Typically, bonding wires are made from gold, aluminum, or copper. Gold wires offer excellent ductility and conductivity. Aluminum wires are cost-effective and widely used. Copper wires have superior strength and electrical conductivity.
The diameter of bonding wire ranges from 15 to 50 micrometers. This small size enables precise connections in compact devices. Studies show that thinner wires reduce resistance and enhance overall performance. However, using very fine wires might lead to issues during bonding. Selecting the correct diameter is essential for reliability.
Bonding ribbons differ primarily in their shape and surface area. Ribbons, often made from the same materials as wires, have a broader surface. This helps distribute stress more evenly across connections. Nevertheless, ribbons can be harder to handle during the bonding process. Reports indicate that their application requires careful considerations. Balancing efficiency and reliability remains a challenge in the industry.
Ribbon is commonly used in microelectronics for various applications, especially in connecting components on chips. The main materials used in ribbon include aluminum and copper. These metals are favored for their excellent conductivity.
The composition of ribbon influences its properties. Ribbons are typically wider and thinner than traditional bonding wires. This allows for efficient space utilization in compact electronic devices. However, the thinness can present challenges in handling. Sometimes, ribbon can be difficult to manipulate. Its fragility might lead to breakage during the bonding process.
Another key aspect is the flexibility of ribbons. This characteristic allows for a wider range of applications. However, it also makes them sensitive to environmental factors like humidity. Left unchecked, this can degrade performance. The manufacturing process seeks to address some of these issues, but flaws can still occur. Understanding these properties is crucial for engineers.
Bonding wires play a crucial role in electronics and packaging. They connect semiconductor chips to substrates. In modern devices, these connections ensure reliability and efficiency. The bond wires are typically made from gold, aluminum, or copper. Each material has its own set of advantages and challenges. For instance, gold wires exhibit excellent corrosion resistance. However, they can be expensive.
Applications of bonding wire have been expanding significantly. According to a market report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global bonding wire market is expected to grow significantly over the next five years. With the rise of 5G technologies and IoT devices, the demand is higher than ever. Bonding wires are essential in maintaining the performance of these devices. Moreover, in automotive electronics, they are crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operations.
Tip: Always consider the operating environment when choosing bonding materials. Different conditions can affect performance. Sometimes, aluminum bonding wire can oxidize faster under certain conditions. Checking compatibility is vital. Another tip is to regularly evaluate the bond wire’s integrity during production. Small issues can lead to significant failures later on. These practices can minimize risks effectively.
Ribbon, a flat and wide metallic conductor, is increasingly used in semiconductor and circuit assembly. Its design allows for higher bonding efficiency. According to recent industry reports, ribbon wire can provide up to 30% improvement in electrical performance compared to traditional bonding wires. This is crucial, as the demand for high-performance electronic devices grows, pushing manufacturers to explore more efficient options.
In semiconductor packaging, ribbon facilitates multi-die connections. This is important for advanced Integrated Circuits (ICs) that require compact designs. A 2023 study highlighted that using ribbon can decrease footprint by 25%. Despite these benefits, there are challenges associated with handling ribbon. Precision in placement is vital, as slight misalignment can lead to bond failure.
Furthermore, manufacturers must consider the impact of ribbon's larger profile on thermal management. While ribbon helps in certain applications, not every circuit assembly benefits from it. Some assemblies still prefer bonding wire due to its flexibility in tight spaces. Balancing performance and practicality remains a key focus for engineers in the field.
| Feature | Bonding Wire | Ribbon |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Gold, Aluminum, Copper | Copper, Aluminum |
| Shape | Single wire | Flat ribbon |
| Applications | Chip to package connections | Surface mount device connections |
| Advantages | High strength, excellent conductivity | Higher current carrying capacity, efficient thermal management |
| Disadvantages | Limited to smaller bond areas | More complex handling and attachment |
| Typical Diameter | 20-50 microns | 50-200 microns |